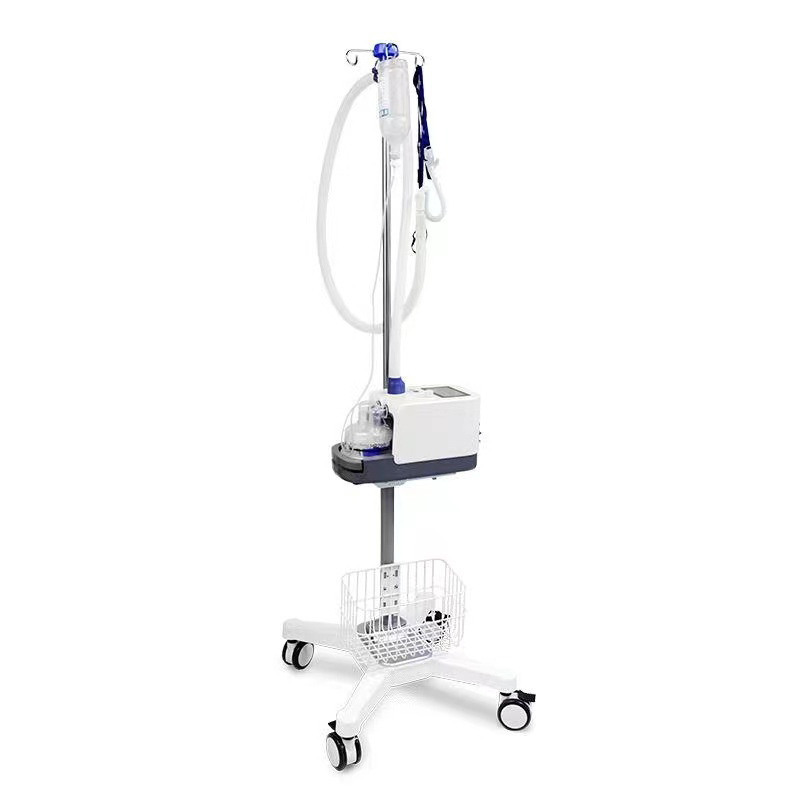
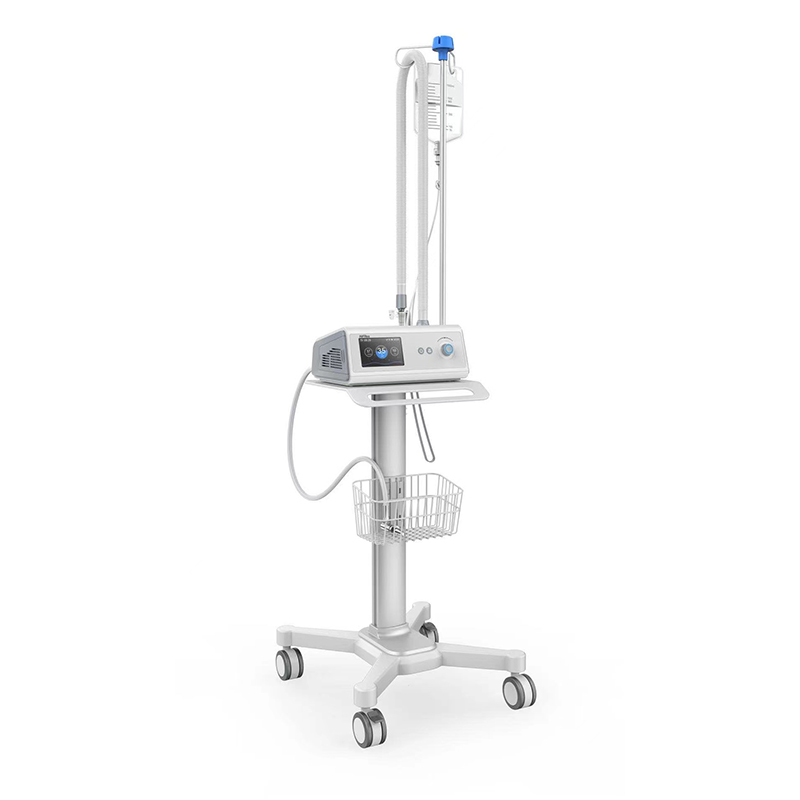
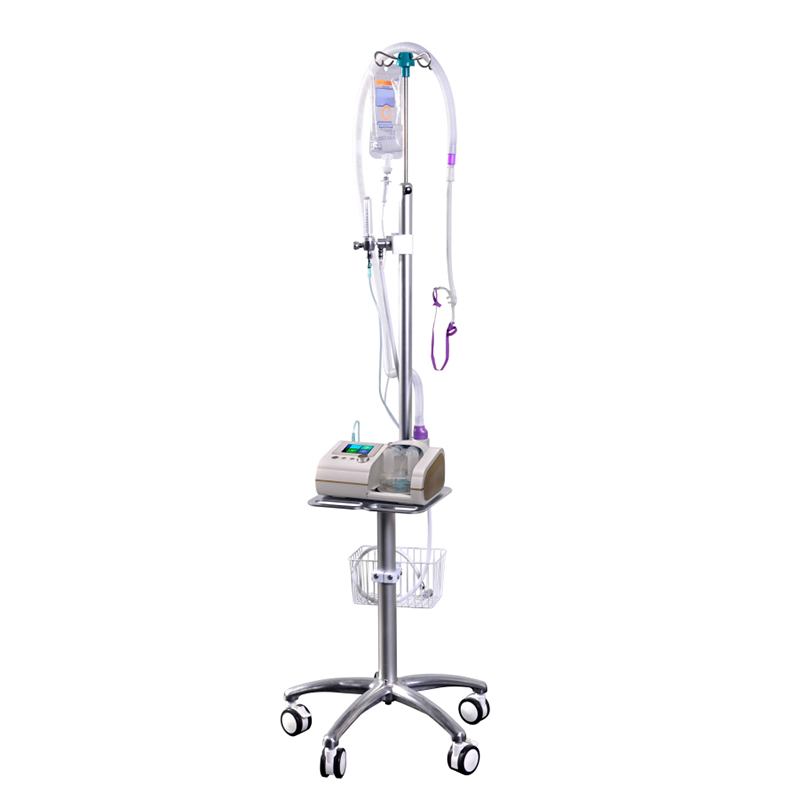
AN-HF8M High Flow Respiratory Humidification Therapy Apparatus
★Precise control of oxygen concentration
★80L/min high flow output
★Real-time monitoring of blood oxygen
★The host does not need to be disinfected
AN-HF8M High-Flow Breathing Humidification Therapy Apparatus uses a soft nasal congestion catheter to deliver up to 80L/min of air-oxygen mixed gas to the patient after heating and humidification, which can effectively improve the patient’s oxygenation level and clear the mucus and cilia. At its best.
Applicable departments: Respiratory medicine, ICU, emergency room, neurology, neurosurgery, cardiothoracic surgery, pediatrics (≥3 kg), rehabilitation ward, geriatric ward, etc.
Clinical features:
Combined with nasal congestion catheter to maintain optimal humidity and ensure comfort
Deliver high-flow mixed oxygen to achieve the following therapeutic effects
Auxiliary oxygen inhalation: maintain a stable high inhaled gas oxygen concentration, improve oxygenation, reduce blood oxygen deficiency, and increase effective alveolar ventilation.
Positive airway pressure: produces low positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), reduces respiratory power consumption and increases respiratory frequency; promotes the opening of alveoli, which is conducive to the diffusion of oxygen.
Reduce dead space: reduce the dead space of the mouth, nose and pharynx, promote oxygen conversion, and improve ventilation efficiency.
Airway humidification: heating and humidifying the gas, improve the mucosal cleaning function, promote the humidification and elimination of sputum, and reduce the chance of infection.
❖Clinical application:
1. Acute patients with mild to moderate respiratory failure in ICU or emergency room
[Improve dyspnea, increase oxygenation, reduce intubation rate, intubation mortality rate is significantly lower than non-invasive ventilation and standard oxygen therapy]
2. Tracheal intubation
[Increase oxygenation index and delay the occurrence of hypoxemia]
3. Oxygen therapy after invasive drug withdrawal
【High tolerance and comfort, reduce reintubation rate】
4. Acute heart failure and cardiogenic pulmonary edema
[Improve dyspnea, especially intractable dyspnea]
5. Postoperative care to reduce the risk of respiratory failure
[Replacement of non-invasive ventilator, higher comfort level]
6. Chronic airway disease
[Improve the upper airway status of patients with obstructive sleep apnea]
Welcome to the website of Henan Anhel Medical Equipment Co., Ltd.!
- Molecular diagnosis
- Rapid Tests
- Drug of Abuse
-
Immunofluorescence
- Urinalysis Tests
-
POCT System
-
ELISA Test
-
DOT Test
-
Chemistry
- Ultrasonic
- Hemodialysis
- Ventilator
- ECG/EEG/EMG
-
Dermatology
- AN-specific electromagnetic wave therapy device
- AN-KL Carbon Dioxide Laser Treatment Machine (Scanning)
- AN high-energy narrow-band red and blue light therapy system
- AN Steam Therapy Fumigation Apparatus
- AN-308nm Excimer Light Skin Treatment System
- AN-5000 308 Home Excimer Phototherapy Apparatus
- AN-LED Home Spectral Therapy Apparatus
- AN 311 Ultraviolet Light Therapy Apparatus
- AN LED Spectrum Therapy Apparatus
- AN Medical Video Wood Lamp
- CT/MR
-
Ophthalmology Department
- AN-BLX5 Dental X-Ray
- AN-BLX10 Dental X-Ray
- AN-BLX8P High Frequency Dental X-Ray
- AN-BLX9 Dental X-Ray
- AN-BLX6 Dental X-Ray
- AN-BLX8 Dental X-Ray
- AN-digital oral X-ray imaging system HDR-500/600
- AN-Visual evoked potential meter M-800E
- AN-AOV-FB Excimer Laser Ophthalmology Treatment Machine
- AN-YZ3 Handheld Slit Lamp Microscope
- Dental
- Hematology Analyzer
- Chemistry Analyzer
-
POCT SYSTEM
- AN-AT1 Touch Screen HD Black and White Ultra
- AN-RS-N50 full digital notebook ultrasound diagnostic instru
- AN-RS-N50 (VET) all-digital notebook ultrasound diagnostic i
- AN-A6 All-digital veterinary B-ultrasound diagnostic instrum
- AN-M6 Veterinary B Ultrasound Diagnostic Instrument
- AN-A10 All-digital veterinary B-ultrasound diagnostic instru
- AN-M10 Veterinary B Ultrasound Diagnostic Instrument